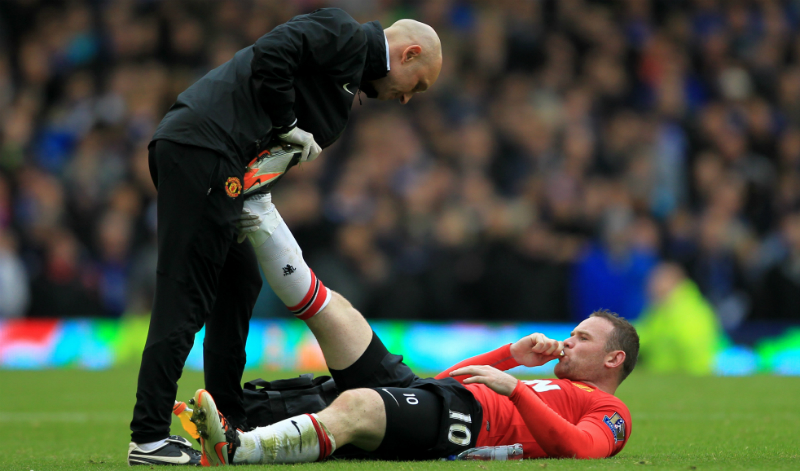
Understanding cramps explains why bodies fail just when pressure peaks.
You might also like

Why Goalkeepers Waste Time Late in Football Matches
19:47 agoCramps occur when muscles contract involuntarily.
Common causes include:
Related Article

How Injuries Are Affecting AFCON Teams and Changing the Tournament Landscape
17:07 ago- Muscle fatigue
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Dehydration
- Prolonged high-intensity running
Football combines all these factors into a single match.
Fatigue Peaks Late in MatchesBy the final minutes:
- Muscle energy stores are depleted
- Recovery time between sprints disappears
- Neuromuscular control weakens
This makes muscles more prone to sudden spasms.
Why High-Intensity Players Cramp Morelikely roles are more affected.
Players who cramp most often:
- Full-backs covering long distances
- Midfielders pressing constantly
- Wingers making repeated sprints
The more explosive work a player does, the higher the cramp risk.
Dehydration Increases Cramp RiskFluid loss impacts muscle function.
During matches:
- Players lose fluids through sweat
- Electrolytes drop
- Muscle signalling becomes less efficient
Even mild dehydration can trigger cramps late.
Why Hot and Humid Conditions Make It WorseEnvironmental factors matter.
Heat and humidity:
- Accelerate fluid loss
- Increase heart rate stress
- Reduce cooling efficiency
Cramps appear earlier and more frequently in tough conditions.
Why Players Cramp After Defending LeadsProtecting a lead is physically demanding.
Late defensive phases involve:
- Constant sprinting back
- Blocking shots and passes
- Holding tense positions
This sustained tension exhausts muscles quickly.
Psychological Stress Plays a RoleMental pressure affects physical output.
Late-game stress:
- Tightens muscles
- Increases inefficient movement
- Reduces relaxation between actions
This contributes to cramp onset.
Why Substitutions Reduce CrampingFresh legs matter.
Substitutions:
- Lower overall team fatigue
- Reduce sprint demand on tired players
- Help maintain structure
Teams with deeper squads cramp less late.
Why Some Cramps Are Genuine, Others StrategicNot all late stoppages are identical.
- Many cramps are real physical failures
- Some are exaggerated to gain recovery time
Both can occur in the same match.
Why Referees Allow Treatment On the PitchPlayer safety is prioritised.
Referees:
- Stop play for visible distress
- Allow stretching and treatment
- Add the time back later
Health takes precedence over flow.
Why Cramps Often Affect One Team MoreCramping is uneven.
It often affects:
- Teams under sustained pressure
- Teams with less squad depth
- Teams defending narrow leads
Workload imbalance leads to breakdown.
Why Fans Associate Cramps With Time-WastingFans become sceptical because:
- Cramps appear late
- Leading teams suffer them more
- Restarts are delayed
However, many cases are genuine fatigue responses.
How This Helps You Read Live MatchesUnderstanding cramps helps fans:
- Anticipate longer added time
- Recognise fatigue patterns
- Expect late defensive mistakes
It explains why intensity drops suddenly.
Final ThoughtsPlayers cramp late in football matches because the sport pushes the human body to its limits. Fatigue, dehydration, and pressure converge just as stakes rise.
In football, the mind may want to continue — but the body sometimes refuses.












No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!